Surface magnetic field, remanence, and magnetic flux are three crucial indicators of magnetic steel performance. They are interrelated yet distinct, and people often confuse them. Today, we will explore their similarities, differences, and mutual relationships.
1. Surface Magnetic Field
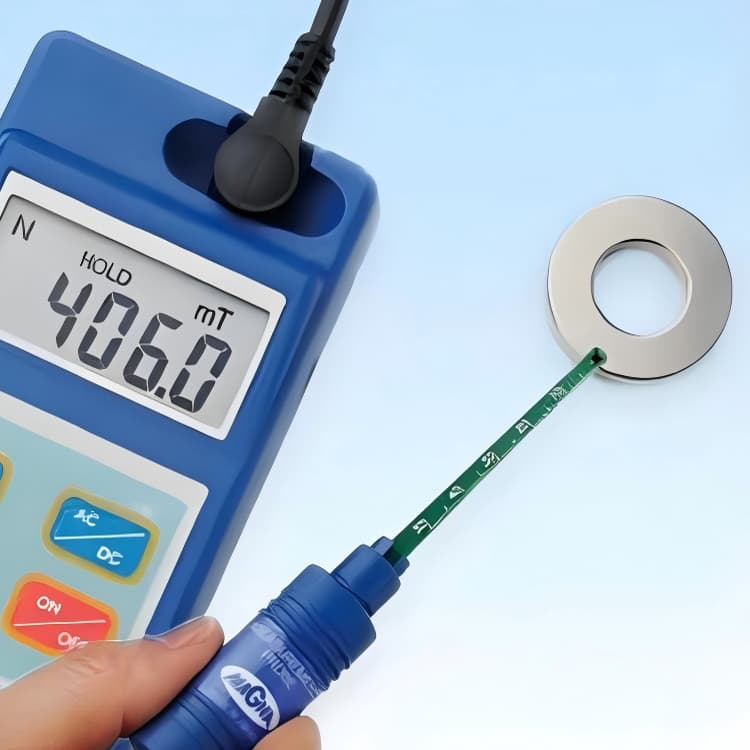
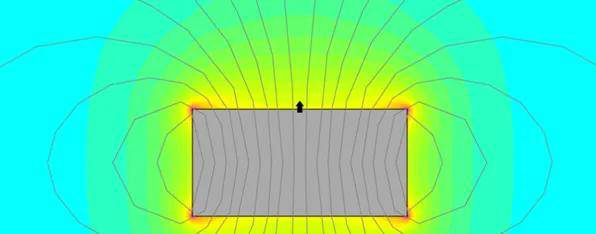
The surface magnetic field refers to the magnetic induction intensity at a specific point on the surface of magnetic steel. We measure it when a gauss meter contacts the magnet, using units in gauss or tesla.
The surface magnetic field varies at different points on a magnet. It is typically lower at the center and higher at the edges. Therefore, it does not fully represent the overall performance of the magnetic steel.
For applications requiring spatial magnetic fields, the surface magnetic field at specific points often serves as an important technical parameter. It is easier to measure than remanence and magnetic flux because gauss meters are relatively inexpensive and simple to operate. Consequently, many buyers use the surface magnetic field as a performance indicator.
Some buyers may not know the exact grade of the magnet but only its maximum or minimum surface magnetic field. In such cases, we can calculate remanence based on the magnet’s shape, size, and surface magnetic field value to infer the magnetic steel grade.
2. Remanence
Remanence refers to the magnetic induction intensity that a magnet retains after an external magnetic field saturates it and gradually reduces to zero. We denote it as BRB_RBR and measure it in gauss or tesla.
The composition and crystal structure of the magnetic steel determine its remanence. For a given magnet under specific conditions, remanence remains constant. Users must use a professional magnetic property detector to measure it, which makes the process challenging.
Relationship Between Remanence and Surface Magnetic Field
If two magnets have identical shapes and sizes, the magnet with higher remanence will also have a higher surface magnetic field. However, if their shapes or sizes differ, the surface magnetic field alone cannot determine remanence. No direct correlation exists in such cases.
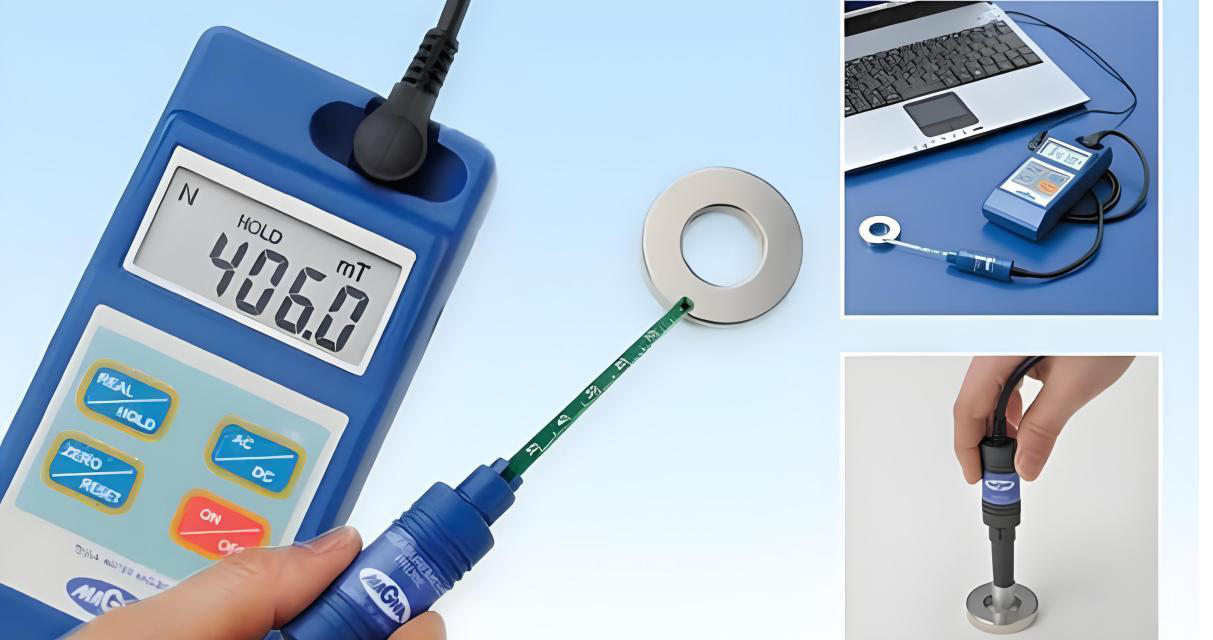

3. Magnetic Flux
Magnetic flux represents the number of magnetic field lines passing through a plane. We denote it as Φ\PhiΦ and measure it in webers (Wb).
Magnetic flux equals the product of the magnetic pole area and magnetic induction intensity. To measure magnetic flux, use a flux meter with a measuring coil.
Unlike the single-point measurement of the surface magnetic field, magnetic flux reflects the overall magnetic performance of the magnetic steel. This makes it a more accurate and reliable performance indicator. When the magnet’s magnetic circuit closes, you can measure magnetic flux and calculate remanence. This method provides more accurate results than using the central surface magnetic field.
4. Comparing the Three Parameters
Among the three performance parameters—surface magnetic field, remanence, and magnetic flux—remanence is an inherent property of the magnet material. It does not depend on shape or size.
In contrast, we measure both surface magnetic field and magnetic flux based on specific magnet shapes and sizes. The surface magnetic field reflects performance at a single point, while magnetic flux reflects overall magnetic performance.
5. Conclusion
If you have further questions about surface magnetic field, remanence, or magnetic flux, leave a comment and engage in discussions with us.







